JAVA - 재귀호출이란?(Recursive Call)
Java에서 메서드를 사용하다보면 메서드 내에서 자신의 메서드와 같은 형태의 메서드를 반복적으로 호출하는 경우가 있습니다. 특히, 수학적인 계산을 할 경우에 말이죠.
1. 재귀호출(Recursive Call)이란?
- 메서드 내에서 자기 자신을 반복적으로 호출하는 것
- 재귀호출은 반복문으로 바꿀 수 잇으며, 반복문보다성능이 나쁨
- 이해하기 쉽고 간결한 코드를 작성할 수 있음
- 재귀함수의 형태로 많이 사용됨.
▶ 재귀호출의 예
팩토리얼(!), 제곱, 트리운행, 폴더목록표시 등등
재귀호출에서 가장 많은 예제로 사용되는 팩토리얼(Factorial)을 구현하여 살펴보겠습니다.
▶ 팩토리얼의 정규식
1
2
3
f(n) = n * f(n-1)
단, f(1) = 1
5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
팩토리얼을 자바코드로 구현하면 아래와 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public long factorial(int n) {
long result = 0;
if (n == 1) {
result = 1;
} else {
result = n * factorial(n - 1);
}
return result;
}
위의 코드에서 중요한 로직은
1
2
3
4
n = 1 이면,
1 을 리턴하고,
n = 1 이 아니면,
n * factorial(n-1) 입니다.
순서1
n = 5 일 때,
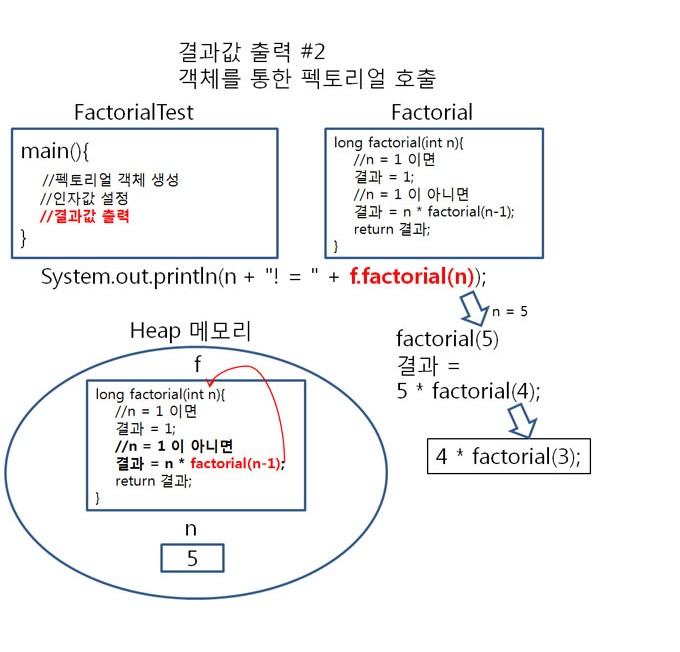
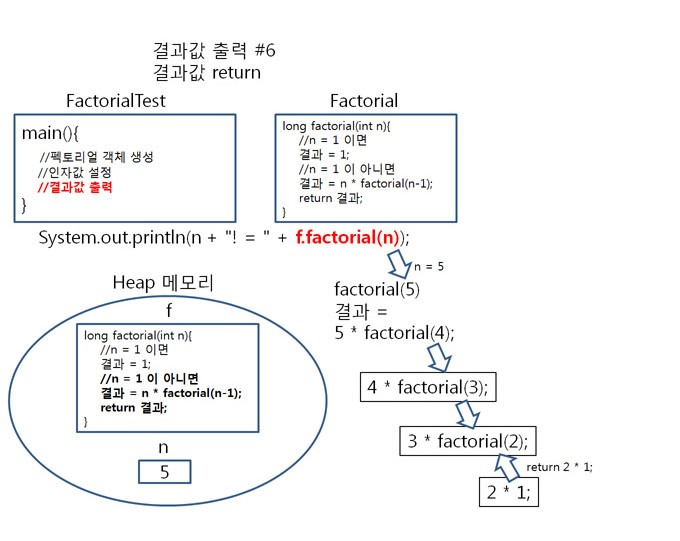
factorial(5)가 호출 되고,5 = 1 이 아니므로 result = 5 * factorial(5-1); 가 됩니다. ( 5-1 = 4 )
result = 5 *
factorial(4); 로 정리됩니다.
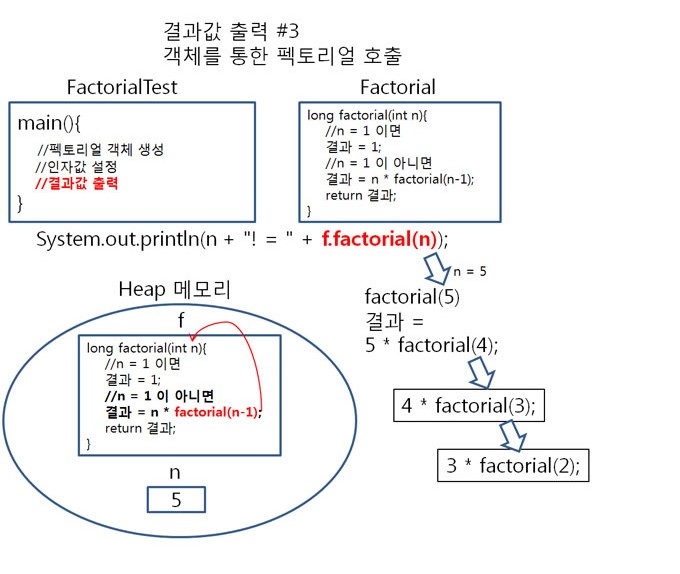
순서2
factorial(4)가 호출 되면,
4 = 1 이 아니므로 result = 5 * 4 * factorial(4-1); 가 됩니다. (4-1 = 3 )
result = 5 * 4 *
factorial(3); 로 정리됩니다.
순서3
factorial(3)이 호출 되면,
3 = 1 이 아니므로 result = 5 * 4 * 3 * factorial(3-1); 가 됩니다. (3-1 = 2 )
result = 5 * 4 * 3 *
factorial(2); 로 정리됩니다.
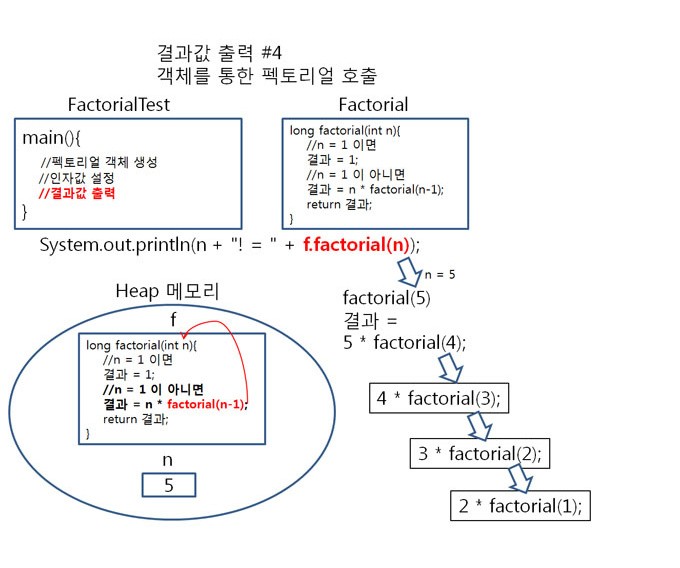
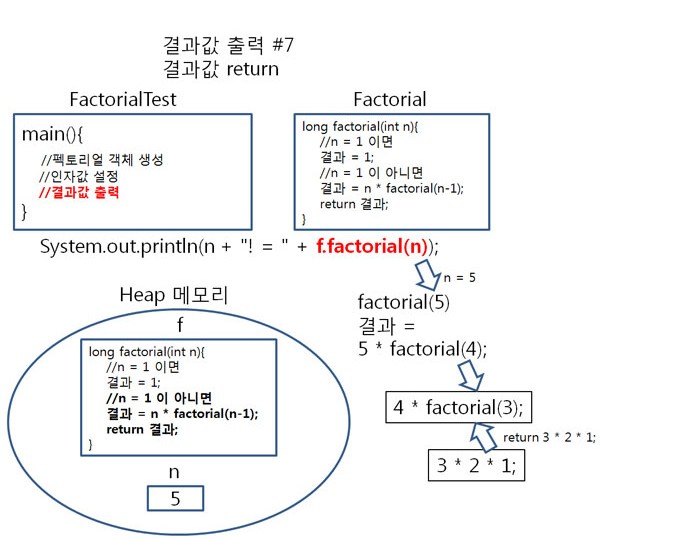
순서4
factorial(2)가 호출 되면,
2 = 1 이 아니므로 result = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * factorial(2-1); 가 됩니다. (2-1 = 1 )
result = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 *
factorial(1); 로 정리됩니다.
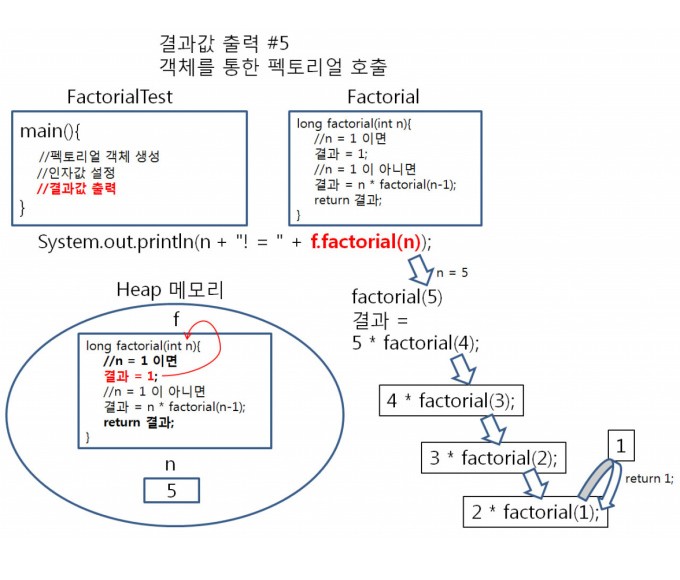
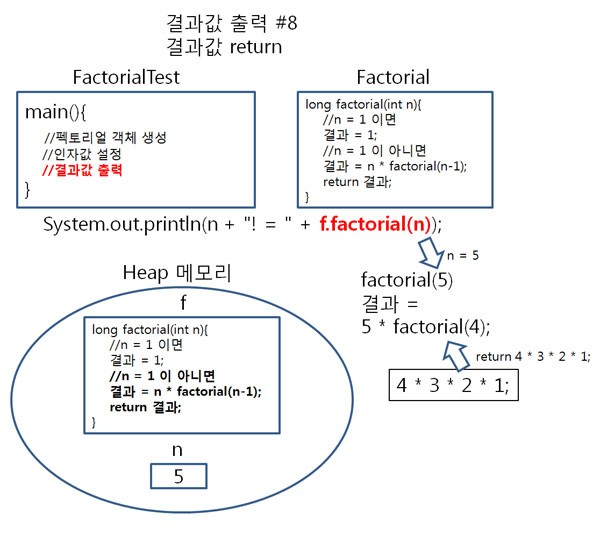
순서5
마지막으로 factorial(1) 이 호출 되고,
1 = 1 이므로 1 이 리턴되어,
result = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * factorial(1); 은 result = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1; 로 정리됩니다.
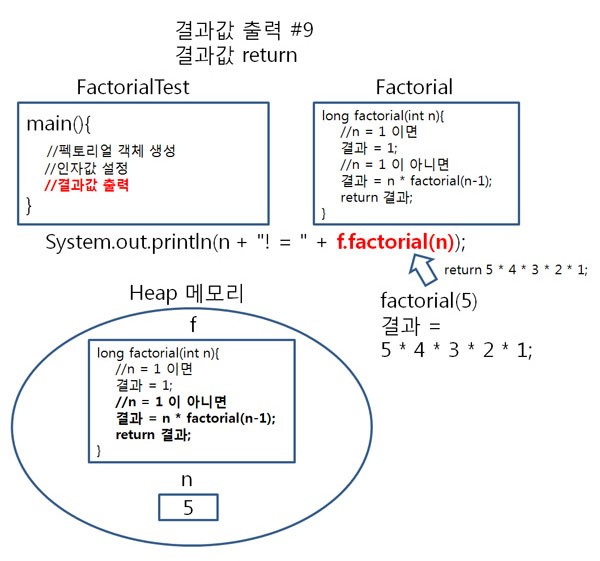
그래서 factorial(5)가 호출되면, result = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 이 리턴되는 것입니다.
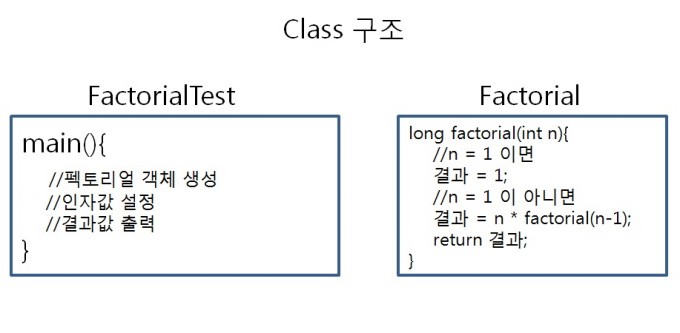
위의 내용을 예제코드와 그림으로 살펴보겠습니다.
▶ 예제코드
Factorial.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* @file name : Factorial.java
* @date : 2013. 8. 15.
* @discription : 팩토리얼 클래스
* @author Cremazer(cremazer@gmail.com)
*/
public class Factorial {
public long factorial(int n) {
long result = 0;
if (n == 1) {
result = 1;
} else {
result = n * factorial(n - 1);
}
return result;
}
}
FactorialTest.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* @file name : FactorialTest.java
* @date : 2013. 8. 15.
* @discription : 팩토리얼 테스트 클래스
* @author Cremazer(cremazer@gmail.com)
*/
public class FactorialTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
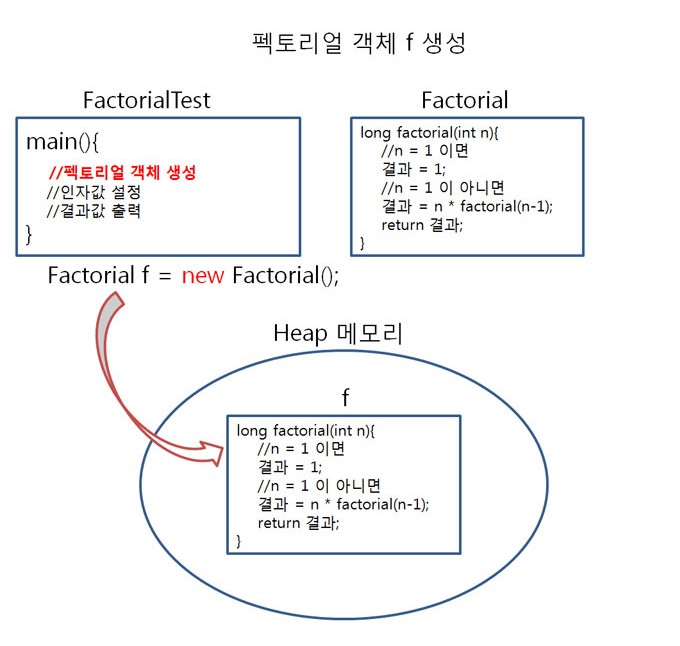
Factorial f = new Factorial();
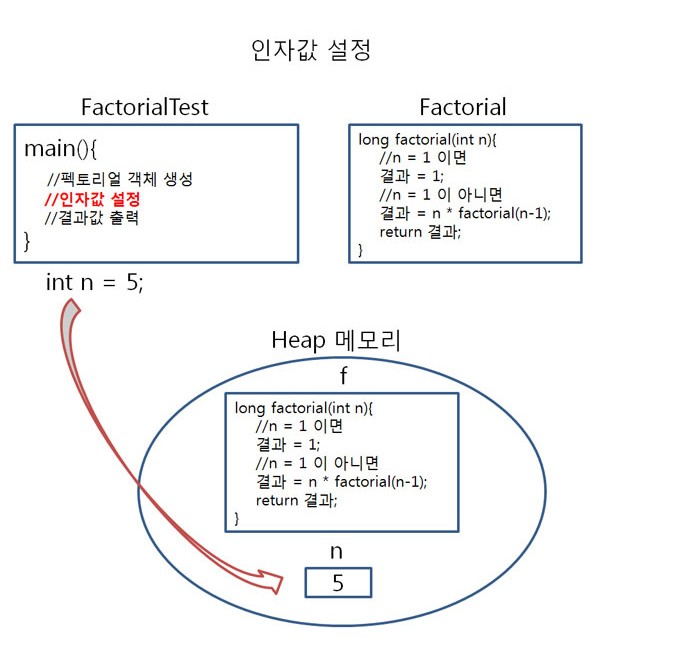
int n = 5;
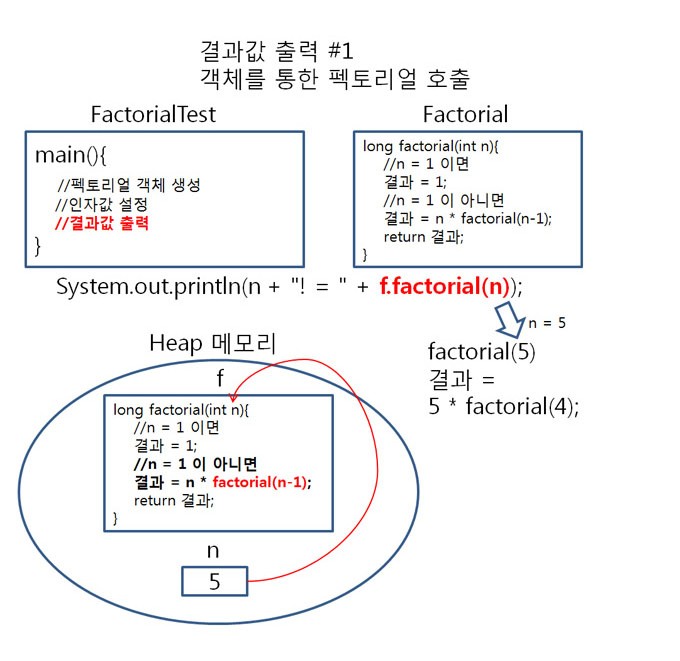
System.out.println(n + "! = " + f.factorial(n));
}
}
▶ 결과
5! = 120
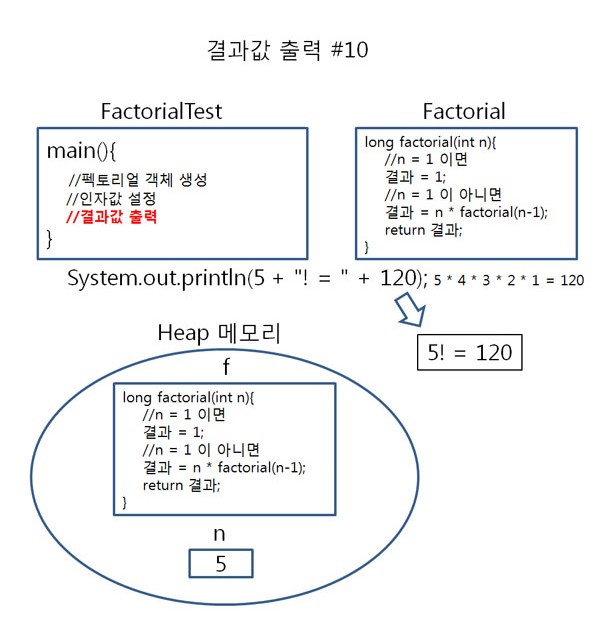
펙토리얼을 테스트 하기 위해 main() 메서드에서 Factorial객체 f를 생성하여 f를 이용해 facltorial(int n)에 접근해 봤습니다.
이 과정을 그림으로 살펴보면 아래와 같음을 알 수 있습니다.
▶ 팩토리얼의 호출 원리